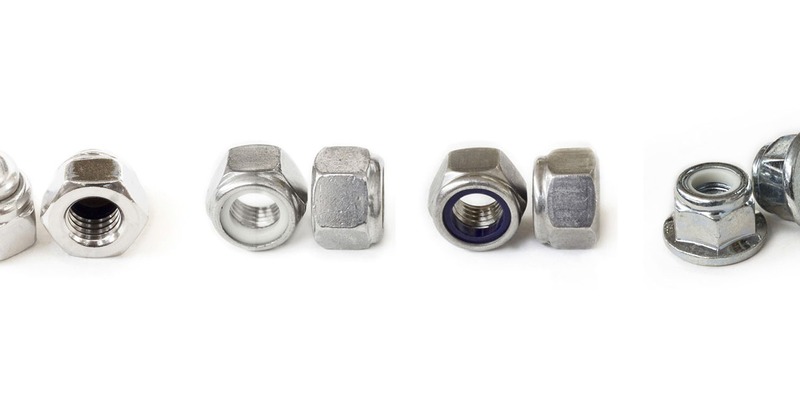
In bolted connections subjected to continuous stresses, there is often a serious risk that the nut may loosen from the screw. For this reason, self-locking (or self-braking) nuts have been developed and designed.
They are recognizable at first glance, thanks to the characteristic presence at the top of a space dedicated to housing an insert, in various types of material, which has the task of preventing the nut from unscrewing.
There are different types of self-locking nuts:
- Fully metallic self-locking nuts
- Self-locking nuts with a nylon insert
- Self-locking flange nut (fully metallic or with a plastic insert)
- Blind self-locking nut with a cap
Fully metallic self-locking nuts are characterized by the radial deformation of the thread, this action occurs under strictly controlled conditions, the diameter of the threading progressively reduces without altering its pitch. The screwing process generates a force that creates a locking moment on the threads of the screw, thus preventing the nut from "losing" adherence. Before being used, the nut is lubricated with specially studied products.
In our range of products, you will find:
- Fully metallic self-locking nut DIN 980 ISO 7042 Form V

- Fully metallic self-locking nut with fine pitch DIN 980 ISO 7042 Form V

- Fully metallic self-locking nut DIN 6924

Self-locking nuts with a nylon insert are recognizable by the presence of a special washer, appropriately sized, in the upper part of the part. The screwing process causes the insert to produce friction on the thread of the screw, generating a constant braking movement, thus avoiding seizure phenomena.
Among our products, you will find:
Self-locking nuts in class 8 and 10 are also available with fine pitch.
Self-locking nuts can also be equipped with a flange, the addition of this detail has the advantage of improving the distribution of the load on the threads and reducing the specific pressure exerted on the support surface.
Also for this item, they can be found on the market in the fully metallic version and with a plastic insert:
- Fully metallic self-locking flange nut DIN 6927 EN 1664

- Self-locking flange nut with plastic insert DIN 6926 EN 1663

The last type available in our product range is the blind self-locking nut with a cap and plastic insert, also available in stainless steel.
Write to us at commerciale@univiti.it to request a quote!
 Added to quote
Added to quote